Financial ratios: The importance of owning a home has been highlighted by COVID-19. Huge unsold inventory and a loss of confidence brought on by the pandemic have ensured that Indian real estate remains a buyer’s market. The dynamics of buying a house are currently most appealing, with decadal lows in home loan interest rates and on-demand availability of ready-to-move-in projects.
To complement your quest for purchase of real estate, here is a list of six essential financial ratios and pointers.
Loan-to-value ratio
One of the key parameters used by lenders to determine the amount and eligibility of a home loan is the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. It’s the portion of the property’s cost that a lender agrees to finance. Lenders use the LTV ratio to determine how risky a loan application is. The maximum LTV for home loans currently ranges from 75 to 90% of the property value. The applicant must cover the remaining balance (down payment).
Banks and HFCs (housing finance companies) will assess home loan eligibility using the following LTV percentage as a rule of thumb.
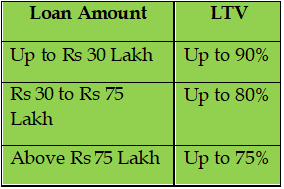
Debt to income ratio
It is possible to use the debt-to-income ratio (DTI) to assess a borrower’s credit risk. Divide the total of all EMIs and credit bills by the borrower’s monthly income to calculate the DTI ratio.
For example, if you pay Rs 8000 for a car loan, Rs 12000 for a personal loan, and Rs 5000 for credit card bills each month, your total monthly debt payments will be Rs 25,000. Your debt-to-income ratio is 25% if your gross monthly income is Rs 100,000.
It is generally recommended that your DTI be kept between 40 and 50 percent in order to meet your day-to-day expenses.
Family net worth
The lender will calculate the total income of all co-applicants and family members to determine the overall credit risk. The lender will also assess your assets and family’s net worth, in addition to your personal income. The amount of your mortgage can also increase by combining stock, mutual fund, retirement, life insurance, and rental income.
Gross and net income multipliers
To determine the maximum amount that a lender will lend, a lender multiplies an applicant’s declared income by the “Income Multiplier.” It should not, however, act as the final criterion for loan eligibility. Because the “multiplier” varies by lender, and other factors such as income, FOIR, and employment stability also influence the bank’s decision.
Rental yield
If you’re looking to buy a rental property as an investment, this is an important metric to consider. You can compare the rental yields of various properties to find the most profitable investment. Divide annual rental income by the property value to get the gross rental yield.
ALSO READ: Market share of banks in individual housing loans up
Capitalization rate
The capitalization rate is another important financial ratios to consider when comparing properties. Subtract all operating costs from the annual rent and divide the result by the property value. Repair costs, taxes, and agent fees are all possible expenses. You can compare the return on investment of properties more effectively with the capitalization rate.
Today’s uncertain economy makes it wise to buy a house your family will use, rather than speculating.

